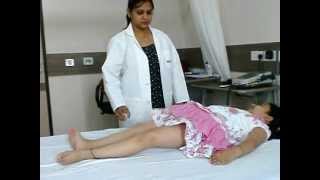
Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy
Data: 2.09.2017 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 559Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy
Posture and Movement of the Child With Cerebral Palsy: : Medicine Health Science Books @ Amazon. com for Children with Cerebral Palsy It is very common to see asymmetry of movement and of posture in a child with cerebral palsy. Because cerebral palsy is a diagnosis of movement and posture, people who have cerebral palsy will have one or more of the following movement disorders. Posture and Movement of the Child Wit, Marcia Hornbrook Stamer, PT, MH, CNDT, PROED Publishing, Inc. eBook Available on RedShelf People with cerebral palsy may have problems swallowing and commonly have eye muscle imbalance, in which the eyes don't focus on the same object. People with cerebral palsy also may suffer reduced range of motion at various joints of their bodies due to muscle stiffness. Cerebral palsy's effect on functional abilities varies greatly. Add tags for Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy. 1 MCWL Introduction to Cerebral Palsy Written and reviewed by the My Child Without Limits Advisory Committee Cerebral palsy (CP) is a term used to describe a problem with movement and posture that makes certain activities difficult. dyskinetic cerebral palsy, 159, dyskinetic cerebral palsy intervention, Eating and Drinking Ability Classi cation System, 4 food choices, hypotonia intervention, 6971 hypotonia, 65, 6971 From Posture and Movement of the Child With Cerebral Palsy, 2nd Ed. Stamer, 2015, Austin, TX: PROED. This book provides clinicians with the detailed information needed to evaluate and treat children with cerebral palsy. It is organized by categories that classify. Learn about a chronic drooling treatment here. Robot suit helps children with cerebral palsy to walk better. improving posture and which lead to movement difficulties. Though many children with cerebral. com: Posture and Movement of the Child With Cerebral Palsy ( ) by Marcia Hornbrook Stamer and a great selection of similar New, Used and. Posture and Movement of the Child With Cerebral Palsy: : Medicine Health Science Books @ Amazon. com The revised edition of Posture and Movement of the Child with Cerebral Palsy has been thoroughly updated with current research information on pathophysiology. Does your child have the signs of cerebral palsy? movement coordination and control, Cerebral Palsy affects posture and balance. Cerebral Palsy: Hope Through Research. NIH Publication Number, updated 5610. Cerebral Palsy, in Batshaw ML, Pellegrino L, Roizen NJ (eds. ), Children with Disabilities, 6th Edition, Baltimore, MD, Paul H Brookes Publishing Company, 2007, pp. For this parameter the authors reviewed available evidence on the assessment of a child suspected of having cerebral palsy (CP), a nonprogressive disorder of posture or movement due to a lesion of the developing brain. Physical Therapy for Cerebral Palsy. Movement issues in children with cerebral palsy can be limited to posture, transitional movements and sensory impairments. Free Online Library: Posture and movement of the child with cerebral palsy. (Brief article, Book review) by SciTech Book News; Publishing industry. Cerebral palsy is a developmental disability that affects movement, posture and coordination. It is caused by brain damage before, during or after birth. Posture and Movement of the Child with Cerebral Palsy: A Guide for Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists Posture and Movement of the Child with. The brain damage is caused by brain injury or abnormal development of the brain that occurs while a childs brain is still developing before birth, during birth, or immediately after. Cerebral Palsy affects body movement, muscle control, muscle coordination, muscle tone, reflex, posture and balance. Cerebral palsy is defined as a group of permanent disorders of the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitation, that are
Related Images:
- The Retail Directory
- Driver Konica Minolta 350zip
- Foxboro 13A Pneumatic Transmitter Manual
- Libro Introduccion Ala Ingenieria De Alimentos Pdf
- 9th grade algebra textbook
- A Package For Mrs Jewels Pdf
- Manual De Uso Overlock Typical
- Emitra rate list 2016 pdf
- Hawaii and kids and travel guide
- Driver Canon LBP 3100b for Win7 64bitzip
- Algebra Arrayan Pdf Gratis
- Avr Microcontroller C Programming Codevision
- Heatseal h425 service manual
- Mainline 1900 Garburator Manualpdf
- 100 Anos de Ma Portuguese Edition
- The Hyperboloid of Engineer Garin The Garin Death Ray
- El Virus Libro Carlos Cuauhtc Shez Pdf
- 2009 Toyota Tundra Owner Manual
- La Cantatrice Chauve Texte Intal Pdf
- Soal Un Bahasa Inggris Sma 2010 Pdf
- Profeziapdf
- Principles Of Managerial Finance 14th Edition
- Kostenlose Atmosfearfx Zombie Invasion Dvd
- Manuale pratico per la progettazione sostenibileepub
- Playstation eyetoy namtai driver
- Elster a1800 pdf download
- VA Top 100 Drum Bass Tracks
- Washington ballet nutcracker tea
- Gaston Hors Serie Tome 5 Le Contrat Lagaffe
- Unity Asset EVIL WATCHER
- Tamil movie mass hindi dubbed download
- Keygen Paradox
- Clown Face With Parabolas Answer
- Panasonic EsLv90 Manualpdf
- Siemens Tk52001 Service Manual
- CM House Roof Patterns Set 1422271
- Colin mcrae dirt mac
- 210 Mw Lmw Turbine Manual
- Free download anime gash bell sub indo
- Inazuma eleven strikers
- Download myob 17 crack
- Lion Spirit Logorar
- Letopisi narnije download skype
- Download movie korea changing partners
- Unimarket eprocurement software download
- Epson Workforce Wf 2630 All In One Printer Manuals
- Livro A Natureza Do ServiSocial Em Pdf
- Color atlas of physiology 6th edition pdf
- Shaolin Chi Kung Pdf
- Build Your Own Benchmark Center
- Einhell Bbh 1500 Manualpdf
- Revival
- Step By Step Polymer Clay In A Day By Emma Ralph
- Amsco Algebra 2 And Trigonometry
- Economics Chapter 4 Demand Answers
- Storia del giornalismo in Italiaepub
- Walter wager 58 minutes ebook
- Rs Aggarwal Maths Class 10 Solution
- Marvins Room
- Smart 1 Universal Tv Txt Classic Manualpdf
- Download garmin software fr60
- Samsung I9500 Efs File
- Multivariable calculus edwards and penney pdf
- Portotecnica Elite 1910m Manualpdf
- Driver Audio Video XP Realtek free Intelzip
- Yamaha Wr 400f P Wr 426f P
- Der Lustmolch Flossen weg
- Terra Nova Test Practice 1st Grade
- Manual De Gramatica Espa Rafael Seco
- Anak tak sah taraf jabatan pendaftaran negara
- Sculpture Today
- John Deere Gator Manual Free
- Satya ke prayog in hindi pdf
- The Woman Who Knew Gandhi
- Manual De Prca Civil Fernanda Tartuce Pdf